Todays juvenile justice system still maintains rehabilitation as its primary goal and distinguishes itself from the criminal justice system in important ways. Ages of Children in Juvenile Detention.

What Is Juvenile Delinquency Definition Theories Facts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
There will be a single judge hearing the case deciding on guilt and providing a punishment.

. Most states consider a juvenile a person between the ages of ten and eighteen however some states set the maximum juvenile age as sixteen. In a juvenile case a judge will determine whether the juvenile is guilty or innocent as well as the appropriate punishments. Instead they have an adjudication hearing.
Though as many as a half of them will not be convicted or will be sent back to the juvenile justice system most will have spent at least one month in the adult jail and one in five of them will have spent. Most states do not even define the juveniles behavior as a crime. Anyone over a states given age limit is tried as an adult.
After the trial the judge sentences the minor to a duration of time in juvenile hall community service or various other types of punishments. A juvenile court matter comes to the courts attention when the police apprehend a minor for violating a statute or a school official parent or guardian refers a problem with a juvenile to the court. With few exceptions in most states delinquency is defined as the commission of a criminal act by a child who was under the age of 18 at the time.
If any of these things give the judge reason to make a punishment more or. There is no jury in this process. The court intake officer then evaluates the case to determine whether further action is necessary whether the child should be referred to a.
In a juvenile trial the accused does not have the same type of trial that an adult would have. While a youth awaits trial he or she may be held in a secure detention facility A judge will determine if the juvenile should be detained before and through the course of the trial and define the intent of the detainment in a detention hearing usually held within 24 hours of the arrest. In most states an individual between the ages of 10 and 18 falls under the juvenile classification.
A juvenile court judge in a criminal case can take other factors into consideration like the age they were when the crime was committed their life at home and their behavior in school. Sometimes children are sentenced to juvenile facilities until they turn 18 and then they are moved to an adult prison. Up to 25 cash back If the juvenile doesnt fulfill these obligations the court may reinstate formal charges.
There is no jury trial. When a juvenile judge sets the case for adjudication he or she is setting it for a trial. Juveniles have a right to a hearing to determine if their case should be transferred to adult court.
In fact in the US the youngest person sentenced to a life sentence was only 12 years old. Pretrial detention is appropriate only when a court believes a youth to be at risk of committing crimes or fleeing during court processing. Additionally some young individuals could face adult classification if the details of their alleged acts indicate that the situation suits an adult trial.
Up to 25 cash back Some juvenile cases are transferred to adult court in a procedure called a waiver Typically juvenile cases that are subject to waiver involve serious offenses like rape or murder or juveniles who have been in trouble before. The Judge of the Juvenile Court sits as the factfinder and renders judgment. Juvenile court fourteen states use more than one method to process juvenile cases1 The independent juvenile court is a specialized court for children designed to pro-mote rehabilitation of youth in a framework of procedural due process.
A juvenile court works like the adult courts in that there is a trial and a hearing for the individual in which the crime and the defendant are taken into consideration. The majority of children in juvenile detention are older teenagers. When kids as young as 9 can be put on trial for severe crimes it is a group of adults that will decide that juveniles fate.
The court may take whatever action it. If the case goes to trial called an adjudicatory hearing in a juvenile case both sides present evidence and the attorneys argue the case much like a criminal trial. Youth under the age of 18 who are accused of committing a delinquent or criminal act are typically processed through a juvenile justice system 1.
It is con-cerned with acting both in the best interest of the child and in the best interest of. A Factfinding Hearing is a trial to determine the facts. Unlike adult court your child is not entitled to a jury trial.
The crimes are called delinquent acts although some of the acts would be called crimes if committed by an adult. The trial is called an adjudication hearing and a judge hears the evidence and determines whether the child is delinquent. If a minor is charged with murder has almost reached the age of majority has a long record of prior criminal activity especially violent crimes like assault and battery and already has received services in the juvenile justice system like counseling and confinement in a juvenile facility a judge likely would decide the minor should be charged as an adult.
If a judge determines that a juvenile has committed the accused crime that is the judge sustains the petition the court can incarcerate the child in an adult prison a juvenile facility or a group home. The United States requires that you be at least 18 to be empaneled onto a jury so having someone judge the content of a case from a different perspective may not result in a fair trial. A youth will typically be detained if he poses a.
The State Prosecuting Attorney presents evidence and bears the burden of proving the allegations of the Delinquency Petition beyond a reasonable doubt. If a crime is particularly. Who is a Juvenile.
Many of the juvenile courts procedures reflect an effort to balance these two concerns and rehabilitate juvenile delinquents. The judge holds an adjudicatory hearing. Juvenile detention is short-term confinement primarily used after a youth has been arrested but before a court has determined the youths innocence or guilt.
Of the juveniles held in adult jails most of them are awaiting trial as 39 states permit or require that youth charged as adults be held in an adult jail before they are tried. In lieu of twelve jurors the juvenile court trials are done by a judge or commissioner who acts as both judge and trier of fact. While similar to that of the adult criminal justice system in many waysprocesses include arrest detainment petitions hearings adjudications dispositions placement probation and reentrythe juvenile justice.
Most states also allow youth to. Children as young as 4 have been arrested for petty vandalism assault or sex-related crimes. However there are areas that may cap that age at 16 rather than 18.
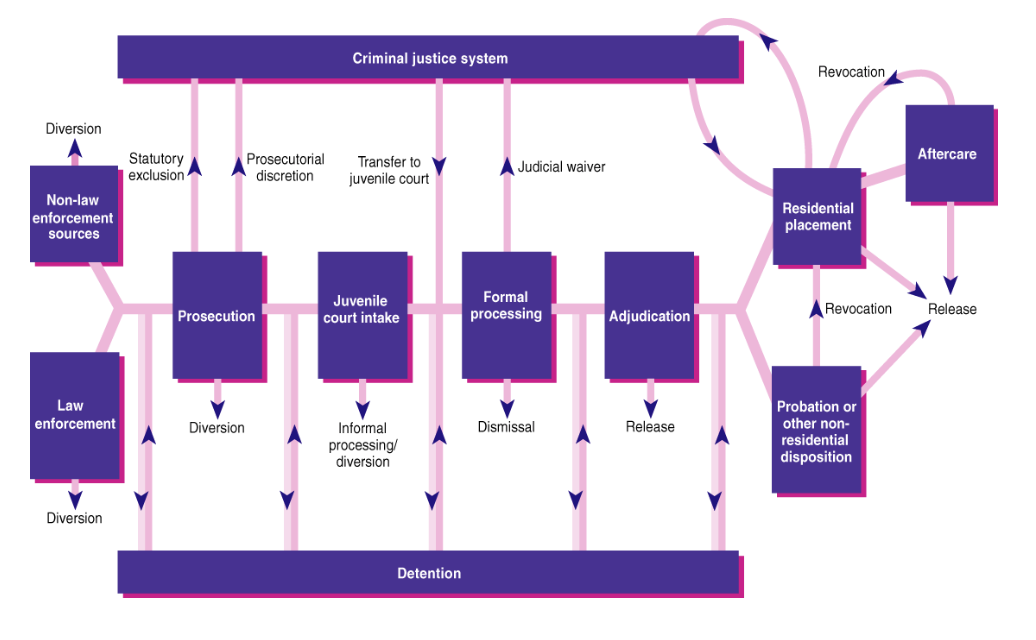
10 10 The Structure Of The Juvenile Justice System Sou Ccj230 Introduction To The American Criminal Justice System

19 Advantages And Disadvantages Of Juveniles Being Tried As Adults Futureofworking Com

0 Comments